by Daksh Bardoliwala
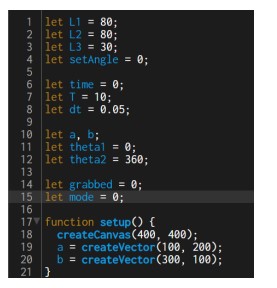
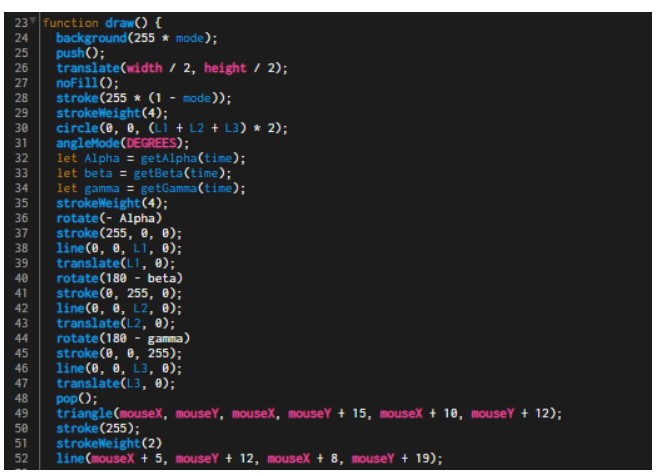
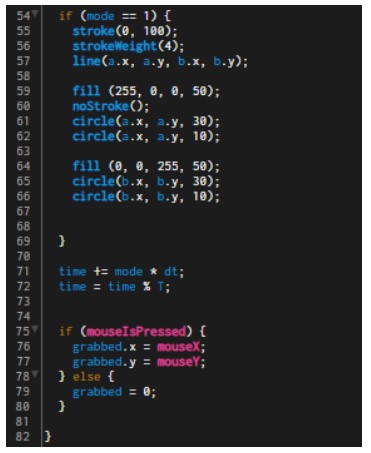
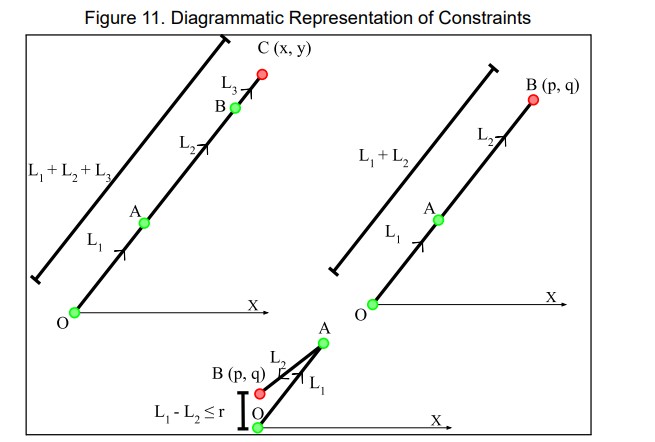
Project Description: This investigation explores the inverse kinematics of a planar robotic arm, emphasizing that all linkages lie within a single plane, simplifying representation to 2-dimensional diagrams. Initially, with 2 linkages, the robotic arm achieves movement in 2 dimensions, constrained by linkage lengths. Adding a third linkage enables the end effector to orient itself in any direction, achieving 3 degrees of freedom: 2 translational and 1 rotational. The project utilized Python to implement algorithms based on abstract mathematical principles, visualizing inverse kinematics and accurately positioning the robotic arm’s end effector. This self-initiated project showcases the learner’s acumen and ingenuity, fulfilling the requirements for a Math Analysis and Approaches Higher Level Internal Assessment.
Project Outcome: Visualization of the phenomenon of inverse kinematics, enabling the precise positioning of the end effector arm of a robot at a designated location.